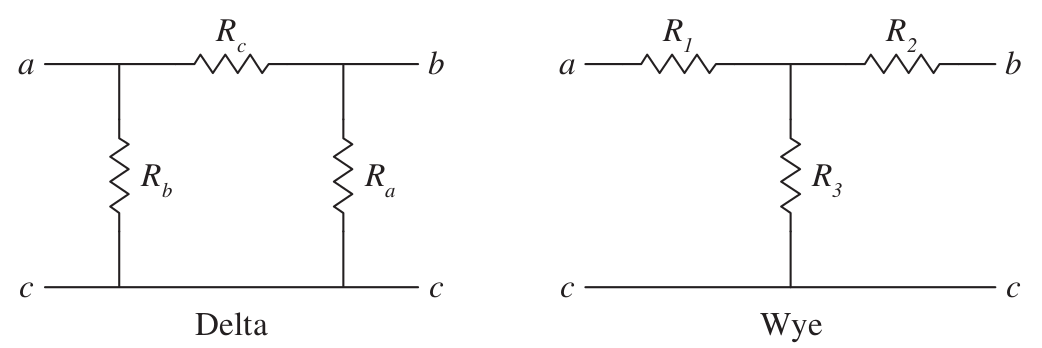Resistive Circuits
Resistivity - Ohm's Law
The resistance of a material can be calculated as:
where \(\rho\) is the resistivity of the material, \(\ell\) is the length, \(A\) is the area. Remember to use SI units (m and m2) to get correect values.
Voltage across a resistor is proportional to current it is carrying.
A short circuit is the case where the resistance between terminals is zero.
An open circuit is the case where the resistance between terminals is infinity.
Series Resistors
The equivalent resistance of any number of resistors connected in series is the sum of the individual resistances.
Parallel Resitors
The equivalent resistance of two parallel resistors is equal to the product of their resistances divided by their sum.

Delta-Wye Transformations
Instead of two terminal equivalents, three terminal equivalents are used.
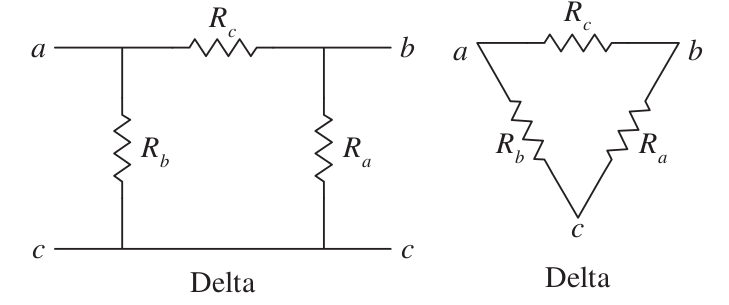
Delta Connections:
The following resistances are equal (Node C can be reduced to one point):
Wye Connections:
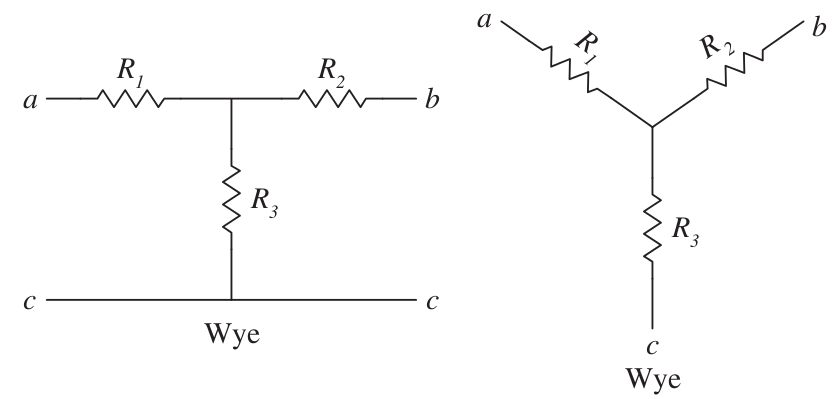
Transformation