Mesh Analysis
In the Mesh analysis the unknown parameters are mesh currents instead of the node voltages.
A mesh is a loop which does not contain any other loops within it.
In the Nodal analysis we have used Kirchhoff's Current Law, in the Mesh Analysis Kirchoof's Voltage Law will be used.
| Nodal Analysis | Mesh Analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| Unknowns | Node Voltages | Mesh Current |
| Method | Kirchoof's Current Law | Kirchoof's Voltage Law |
| Supernode/ Supermesh | Voltage Sources | Current Sources |
Mesh analysis can only be applied to planar circuit. A planar circuit can be drawn with no branches crossing one another.
Method includes the following steps:
- Label each mesh in the circuit.
- Write KVL equations for each mesh.
- Solve equations for the mesh currents.
Things to be careful:
- Although, the direction of mesh currents (clockwise or counterclockwise) is arbitrary, and the equations are valid for both directions, it is conventional to use clockwise current direction.
- Use - sign if you encounter the negative polarity of the voltage source first, use + sign otherwise.
Example 1:
Find the branch currents.
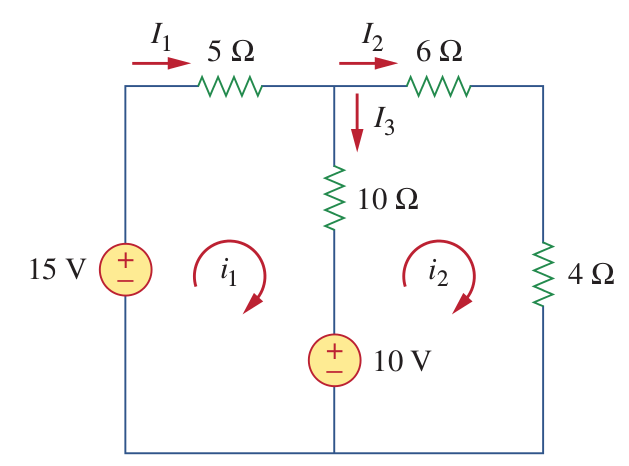
Write the KVL equations for each mesh:
Mesh1:
which is equal to:
Mesh2:
Using the substitution method:
The branch currents are:
Thus:
Example 2:
Find the branch currents
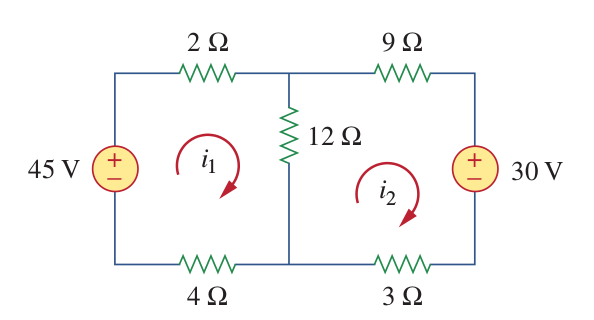
Mesh1:
Mesh2:
Example 3:
Use mesh analysis to find Io.
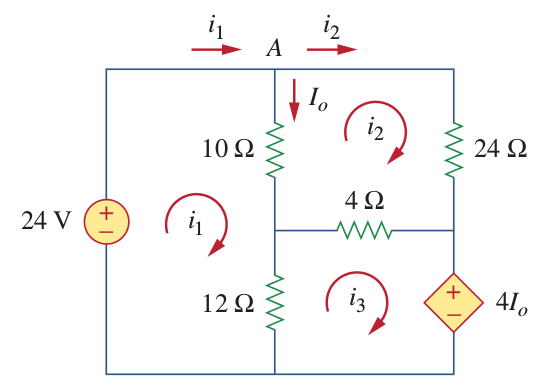
Write KVL equation for each mesh:
Mesh 1:
Mesh 2:
Mesh3:
Io equals to:
Thus:
which is equal to:
Thus:
We need to find Io, which is equal to:
Try to solve the same problem with node voltage analysis.
Example 4:
Use mesh analysis to find Io.
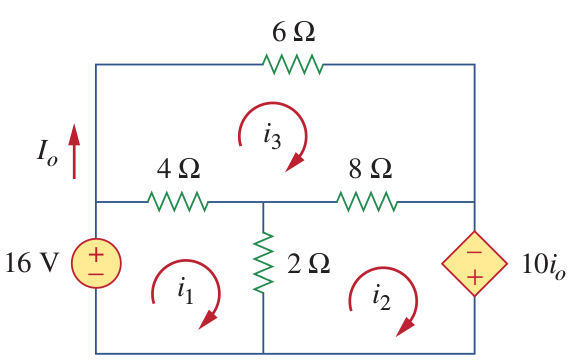
Mesh 1:
Mesh 2:
Mesh 3: